Anthropogenic Noise
⇒ 2025 DATA CALL on Noise Data in the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions
Underwater noise is widely recognised as a threat for marine wildlife and the conservation of endangered species such as several species of cetaceans. The main sources of impulsive underwater noise identified as causing impacts to cetaceans are :
- Seismic surveys
- Pile driving
- Explosive use
- Low and mid-frequency active sonar
Reaction to noise depends on such factors as species, individual, age, sex, and behavioural state. Observed responses to noise in cetaceans are behavioural disturbance, avoidance or abandon or portions of habitats, injuries and damages to hearing and other tissues.
Such responses could result in impacts such as decreased foraging success, higher energetic demands, decreased reproduction. Such impacts can affect populations.
Joint Noise Working Group CMS/ACCOBAMS/ASCOBANS (JNWG)
The Joint Noise Working Group (JNWG) will support the Parties, scientific and advisory bodies and Secretariats of CMS, ACCOBAMS and ASCOBANS in the implementation of the mandates of relevant Resolutions of all three organizations, such as CMS Resolution 12.14 and Decisions 13.58-13.60, ACCOBAMS Res 2.16, ACCOBAMS Res.3.10, ACCOBAMS Res.5.15, ACCOBAMS Res.6.17, ACCOBAMS Res 7.13, ASCOBANS Res.6.2, ASCOBANS Res.9.1, ASCOBANS Res.8.11(Rev.MOP9), and any relevant Resolutions still to be passed.
Initiatives led by ACCOBAMS
Policy-oriented initiatives:
Resolutions 2.16 (2004); 3.10 (2007): 4.17 (2010); 5.15 (2013); 6.17 & 6.18 (2016); 7.13 (2019); 8.17 (2022); 9.15 (2025). Such Resolutions support the implementation of measures for balancing human activities at sea and cetacean conservation.
Mediterranean Strategy on Underwater Noise Monitoring. This work aims, in collaboration with the Barcelona Convention, at laying down the methodological basis for a future implementation of a basin-wide monitoring programme on underwater noise.
Stakeholder involvement:
The Methodological guide: Guidance on underwater noise mitigation measures was developed in 2013 then reviewed in 2016, 2019 and 2022. This guide was conceived to support the implementation of noise mitigation measures by industry, and is the result of a cooperation between representatives of the industry, scientists and NGOs.
The Joint ACCOBAMS-ASCOBANS workshop with navies on underwater noise and cetaceans took place on the 26 & 27 November 2024 in Toulon, France. The objectives of the workshop were to exchange information on best practice experiences and activities, to promote collaboration, and to discuss steps towards improved exchange of information. This joint workshop gathered national navies from the ACCOBAMS and ASCOBANS Areas, NATO, and a limited number of experts from the Joint Noise Working Group (JNWG) of CMS, ACCOBAMS and ASCOBANS, the ACCOBAMS Scientific Committee, ASCOBANS Advisory Committee, and the ASCOBANS Jastarnia and North Sea Groups.
Research projects
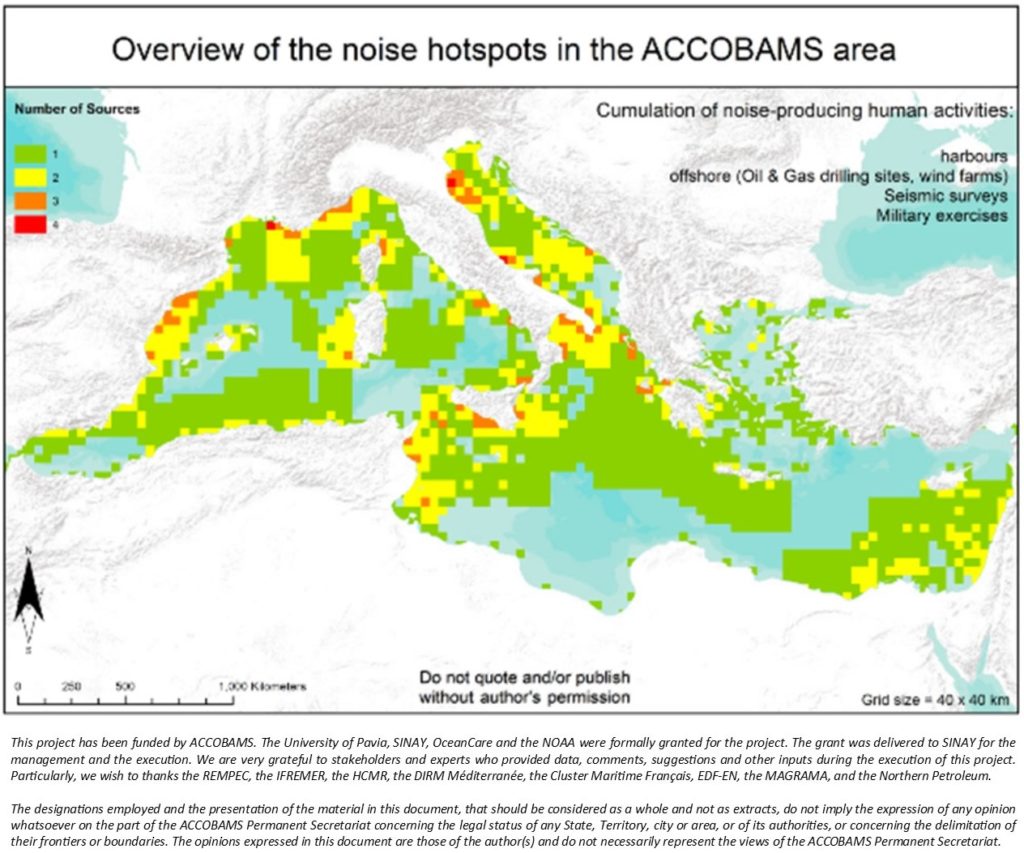
The “Overview of the Noise Hotspots in the ACCOBAMS area” is a project launched in 2015 with the aim of producing the first overview at the Mediterranean scale of the extent of noise-producing human activities.
Results of this project will support decision making on conservation measures for cetaceans. Further, as noise is a form of pollution, results of this project are highly relevant for the objectives of the Barcelona Convention, and particularly in the framework of the EcaP (Ecosystems Approach) initiative.
Document: Overview of the Noise Hotspots in the ACCOBAMS area – Part I the Mediterranean Sea
Improving mitigation measures
An ACCOBAMS label for Marine Mammal Observers (MMOs) is currently under development. This label aims, in collaboration with the JNCC, at certifying high quality training courses for MMOs.





